
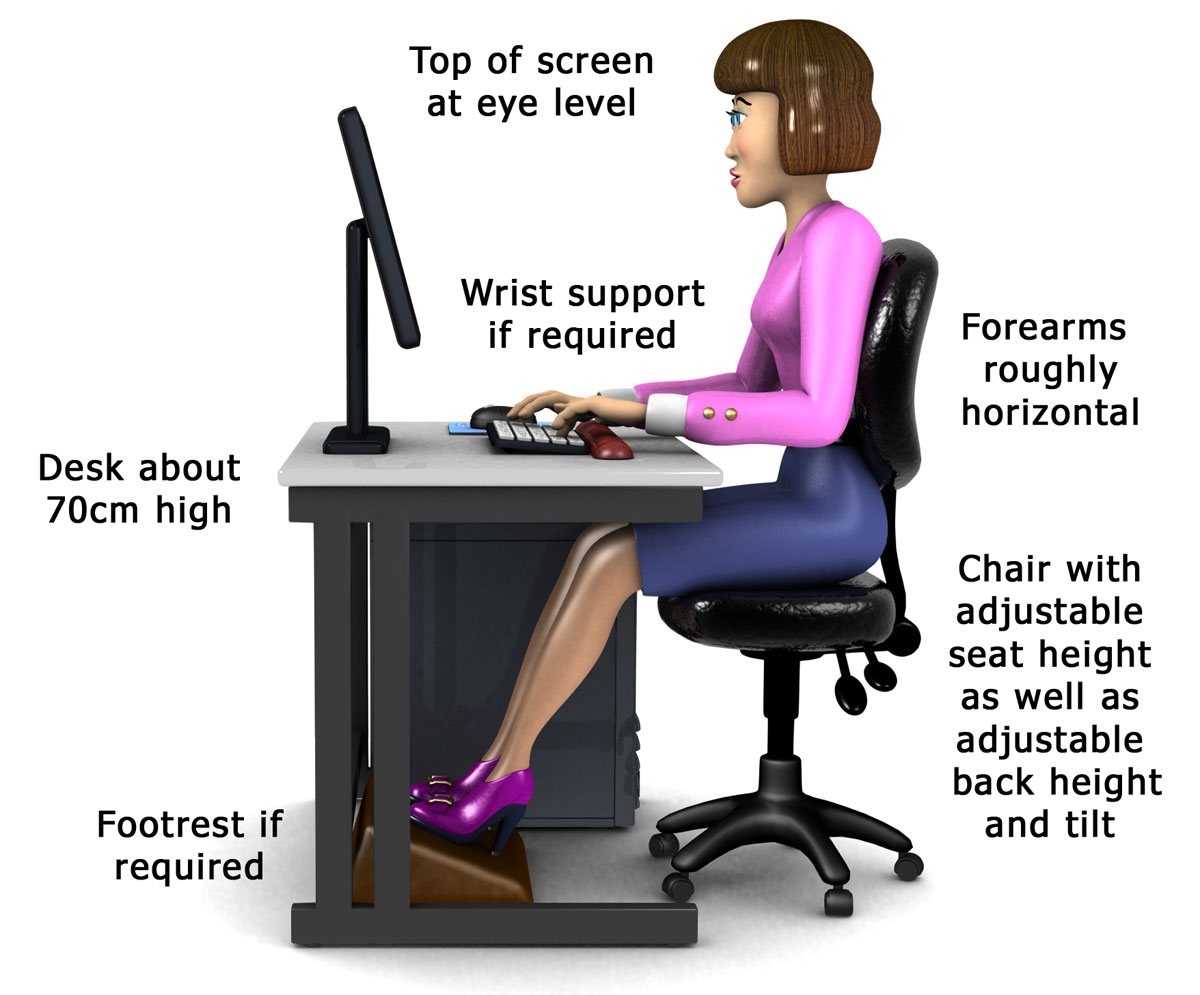
Prolonged use of a screen can cause visual fatigue and eye strain, so it’s important to look after your eye health. Stand on your tiptoes and stretch upwards, as tall as you can, to release some of the tension in your ankles, legs, back, arms and neck.Stand up and march on the spot for 30 seconds to improve the blood flow in your legs.Rotate your ankles round in circles under the desk, first one way and then the other.Make sure that there’s enough space to change position and stretch your legs out every now and then, too. Use a footrest underneath your desk if you need more support, or if the chair is putting pressure on your thighs. Your desk chair should be positioned so that you can sit comfortably with your feet flat on the floor and your lower legs vertical. Interlock your fingers and then push them out in front of you, with palms facing out.Stretch your arms out to the side as far as you can and then above your head as high as you can to stretch your arms, wrists and back.Reach your arms out in front of you and draw big circles with your wrists, first in one direction and then the other.


If you have to bend your wrists upwards to reach the keyboard then use a wrist support, otherwise you are at risk from a repetitive strain injury. This desk support helps prevent your arms from becoming tired or achy. Push your computer screen and your keyboard back a bit if necessary. There should be enough room in front of your keyboard to support both your forearms and your wrists on the desk.
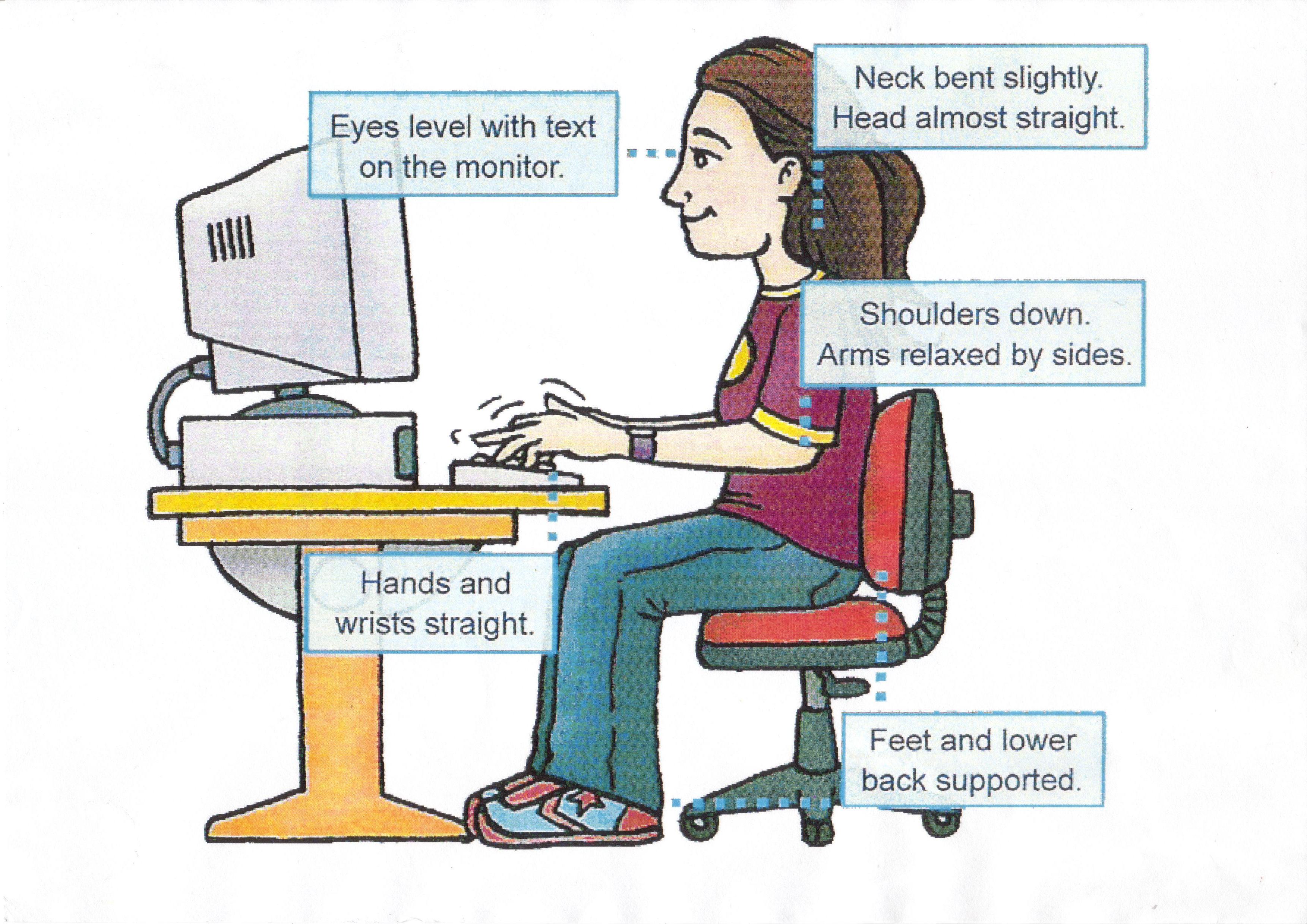 Slowly bring your chin down to your chest, hold for 3 seconds, and then release. Move your shoulders around in small circles, first in one direction and then the other. Sit up straight and slowly tilt your head down to one shoulder and then to the other to stretch your neck. Reduce tension by regularly moving your neck and shoulders: If you ever have to angle your head upwards or downwards to see the screen, then tension can build up in your neck and cause headaches and fatigue. Adjust the tilt and height of your screen or your chair if you need to and, if you have a laptop, you should use a stand to raise it up. Your eyes should be level with the top of your monitor. Stand up and put your hands together, elbows out, then slowly twist to the left and then to the right.Īlso, keep your neck straight as much as possible. Slowly lean your torso over to one side of the chair and then the other to stretch your sides and spine. Stand up and walk around every hour or so, so that you’re not sat in the same position all day. Your lower back (lumbar) should be supported by the chair or a cushion so that sitting upright doesn’t feel uncomfortable or unnatural. Avoid slouching down into your chair or leaning forward onto the desk, as this can cause strains, aches and pains. When sat in your desk chair, your spine should be in an upright position. Each section outlines the best way to sit and gives a few examples of ways to stretch, relax and improve your overall wellbeing. Take a look at the following tips to help improve your posture when working at your computer. Carrying out tasks for long periods without suitable rest breaks. If you’d like to learn more about display screen equipment health and safety, take a look at our online DSE Training. The course covers everything you need to know about legal responsibilities, correct workstation set-up and risk assessment.
Slowly bring your chin down to your chest, hold for 3 seconds, and then release. Move your shoulders around in small circles, first in one direction and then the other. Sit up straight and slowly tilt your head down to one shoulder and then to the other to stretch your neck. Reduce tension by regularly moving your neck and shoulders: If you ever have to angle your head upwards or downwards to see the screen, then tension can build up in your neck and cause headaches and fatigue. Adjust the tilt and height of your screen or your chair if you need to and, if you have a laptop, you should use a stand to raise it up. Your eyes should be level with the top of your monitor. Stand up and put your hands together, elbows out, then slowly twist to the left and then to the right.Īlso, keep your neck straight as much as possible. Slowly lean your torso over to one side of the chair and then the other to stretch your sides and spine. Stand up and walk around every hour or so, so that you’re not sat in the same position all day. Your lower back (lumbar) should be supported by the chair or a cushion so that sitting upright doesn’t feel uncomfortable or unnatural. Avoid slouching down into your chair or leaning forward onto the desk, as this can cause strains, aches and pains. When sat in your desk chair, your spine should be in an upright position. Each section outlines the best way to sit and gives a few examples of ways to stretch, relax and improve your overall wellbeing. Take a look at the following tips to help improve your posture when working at your computer. Carrying out tasks for long periods without suitable rest breaks. If you’d like to learn more about display screen equipment health and safety, take a look at our online DSE Training. The course covers everything you need to know about legal responsibilities, correct workstation set-up and risk assessment.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
